NutriVax project
- In sub-Saharan Africa, millions of children face a dangerous cycle: malnutrition weakens their immune systems, increasing the frequency and severity of infections.
- In turn, diseases further deteriorate their nutritional status. This vicious circle has devastating effects on children’s growth and survival.
- NutriVax is exploring an innovative solution: using nutritional supplements as an incentive for families to vaccinate their children. This approach could save lives, prevent malnutrition, and improve child health in the long term.
The NutriVax trial is a cluster-randomized controlled trial conducted in Yobe State, in northwest Nigeria.
The project is led by ALIMA, in partnership with:
- PAC-CI program (Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire)
- Yobe University Hospital
- GHiGS team from the Bordeaux Population Health Research Center (Inserm, IRD, University of Bordeaux)
Context and challenges
A high-risk region
Yobe State is particularly affected by malnutrition and under-immunization. According to Nigeria’s 2024 Demographic and Health Survey (DHS):
- 10.1% of children suffer from acute malnutrition
- 2.6% are affected by its severe form
- 54.2% are stunted
- Only 59% of children have received a first dose of the measles vaccine, while 40% have not received any dose.
💡 Why is NutriVax a priority?
By combining nutrition and immunization, NutriVax’s goal is to create a virtuous circle: improving health, increasing vaccination coverage, and preventing severe forms of malnutrition among the most vulnerable children.
ALIMA's actions
💡 What are the project’s main activities?
NutriVax is being rolled out across 20 areas of Yobe State, divided into two groups:
- Standard areas: immunization and nutrition awareness
- Intervention areas: in addition to awareness-raising, children receive a 12-month supply of SQ-LNS nutritional supplement
Goal: to reach over 20,000 children aged 6 to 23 months.
An innovative approach
What makes NutriVax unique is the pairing of nutrition supplementation and vaccination. Neither the SQ-LNS nutritional supplement nor vaccination are new. But together, they could mutually enhance their impact.
The study includes four components:
- Two vaccination surveys: conducted at the start and after 12 months, to assess vaccination coverage and the prevalence of malnutrition
- One longitudinal follow-up: tracking 600 children to monitor nutritional and vaccination progress
- One cost-effectiveness analysis: to assess program costs
One qualitative study: using interviews and focus groups to understand the barriers and drivers to vaccination
Ultimate goal: to build evidence to promote sustainable funding for integrated nutrition and immunization programs in highly vulnerable contexts.
The results are expected by the end of 2025.
FAQ
It is a type of trial in which participants are divided into groups (called “clusters”) rather than individually. In the NutriVax study, randomization was carried out by health zones (“wards”).
SQ-LNS stands for Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements. These are ready-to-use, nutrient-dense dietary supplements designed to prevent malnutrition and improve growth and immunity in young children.
On the ground
Related news
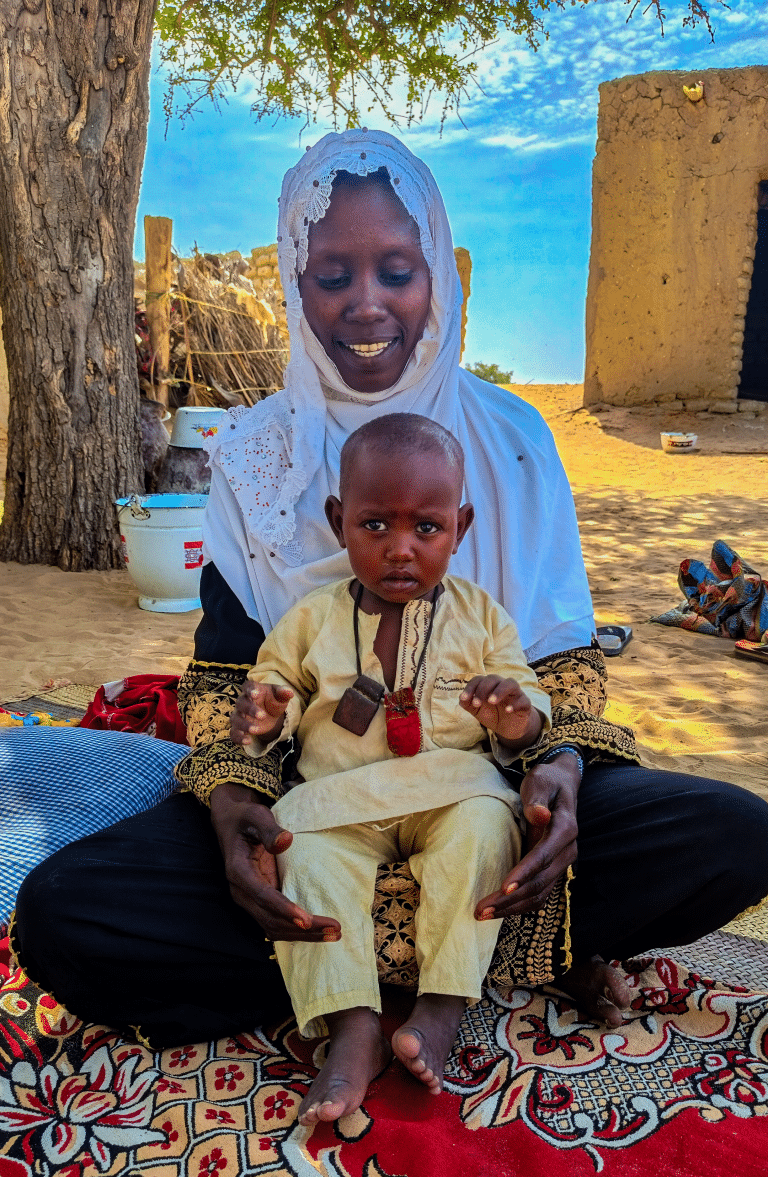
One Sachet, One Chance – Mariam and Hassan’s Journey
In the N’Gouri district, the OptiMAx project combines vaccination with nutritional supplementation to encourage families to return to health centers. Through a mother’s journey, we

OptiMA Trials: When Clinical Research Adapts to Field Realities
In the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Niger, the OptiMA clinical trials successfully combined scientific rigor with operational constraints in complex humanitarian settings. An
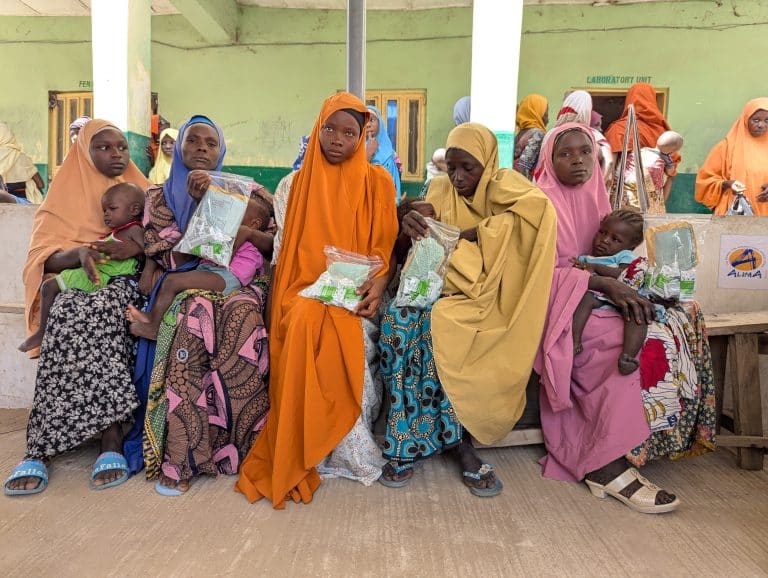

NutriVax: Integrating Nutrition and Vaccination to Save Children’s Lives in Nigeria
Every year, millions of children in Africa are trapped in a vicious cycle of malnutrition and infectious diseases. But what if we could fight both


