Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection that affects the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This disease can be viral, fungal, or bacterial, and poses a significant risk for infants, adolescents, and vulnerable adults. In Africa, meningitis is both endemic and epidemic, especially in the African Meningitis Belt.
ALIMA (The Alliance for International Medical Action) is fighting against this disease through vaccination campaigns, rapid treatment, and epidemiological surveillance.
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, which can be caused by viruses, fungi, or bacteria. It can affect people of all ages, though children and adolescents are particularly at risk.
Types of meningitis
Fungal meningitis
- Rare, but serious
- Affects immunocompromised people (e.g., HIV)
- Treatment: high-dose antifungals
Viral meningitis
- The most common form, caused by enteroviruses
- Flu-like symptoms
- It often resolves on its own
Bacterial meningitis
- The most severe form, caused by meningococcus or pneumococcus
- Medical emergency: can be fatal without immediate antibiotic treatment.
How is meningitis transmitted?
Transmission methods vary depending on the pathogen.
- Saliva droplets (from coughing, sneezing, kissing)
- Close contacts and overcrowded environment
- Pre-existing ENT infections (sinusitis, ear infections)
- Healthy carriers who spread the bacteria without showing symptoms
Risk factors
- Precarious living conditions
- Lack of vaccination
- Weakened immune systems
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
Symptoms should be managed immediately.
In adults and children
- High fever
- Stiff neck
- Severe headaches
- Photophobia (sensitivity to light)
- Mental confusion, seizures
- Vomiting
In infants
- Bulging fontanelle
- Irritability, continuous crying
- Difficulty feeding
- Rigid or floppy body
Without prompt treatment, meningitis can lead to serious neurological complications or be fatal.
Take action
Support the fight against meningitis
Your contribution helps provide vaccinations and care for the most vulnerable populations.
Prevention and treatment
Diagnosis and management
Rapid diagnosis is crucial and typically involves a lumbar puncture to analyze cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatments based on the cause of meningitis
- Viral meningitis: rest, painkillers, hydration
- Fungal meningitis: high-dose antifungals
- Bacterial meningitis: emergency intravenous antibiotics
Vaccination: the best protection
The WHO recommends vaccination against the bacteria responsible for meningitis:
- Meningococcal (serogroups A, B, C, W, Y)
- Pneumococcus
- Haemophilus influenzae type B
Meningitis in Africa: a health challenge
The African Meningitis Belt, stretching from Senegal to Ethiopia, frequently experiences epidemics, requiring urgent vaccination campaigns.
Epidemic impacts
- High mortality without immediate treatment
- Severe neurological consequences (hearing loss, motor impairments)
- Rapid health responses needed to contain outbreaks
ALIMA's commitment in the fight against meningitis
Emergency interventions
- Epidemiological surveillance
- Healthcare worker training
- Prepositioning of medical supplies for rapid response
- Mass vaccination during epidemics
Prevention and treatment
- Early case detection
- Immediate hospital treatment
- Public awareness campaigns
On the ground
Related news
Three Months to Eradicate Ebola: The Power of Collective Action in Kasai
After three months of collective mobilization, the 16th Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was declared over on November 30, 2025.
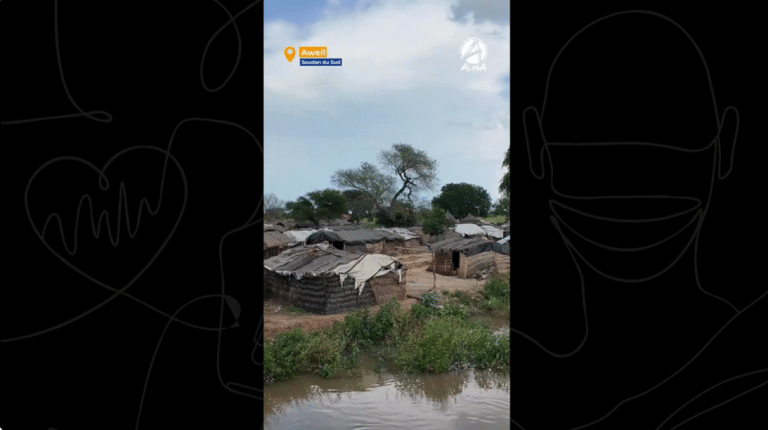

South Sudan: when the climate crisis becomes a health crisis
In Aweil, recurring floods cut off entire villages. Malaria, diarrhea, pneumonia: children are on the front lines. Since 2025, ALIMA has been deploying an emergency
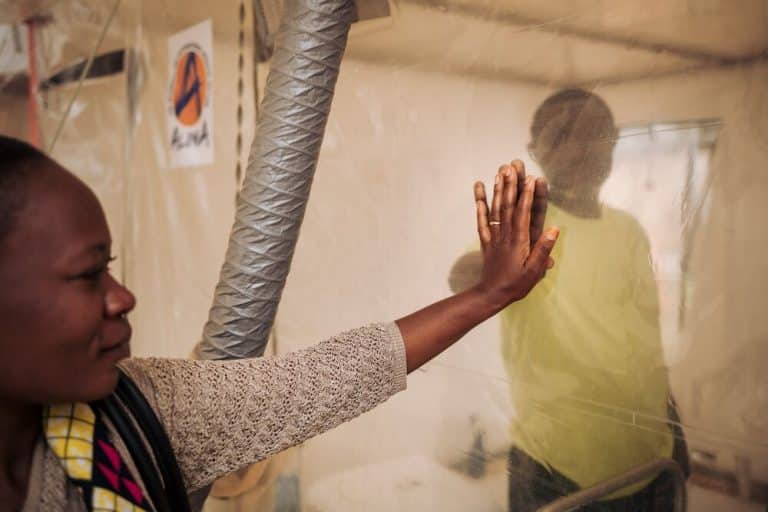

Ebola in Kasai: A Race Against Time!
Since late August, a new Ebola outbreak has struck Kasai in the Democratic Republic of Congo. With 40 deaths already and more than 1,400 contacts


