Emergency response
- 150,000 displaced people in Niger and Burkina Faso received emergency medical assistance in 2019.
- 27 emergency assessments were conducted to identify and respond to health crises.
- Over 10 countries of intervention to provide life-saving care during epidemics, conflicts, and natural disasters.
In times of crisis, every second matters. ALIMA deploys a rapid and effective response to reduce mortality and protect the most vulnerable.
➡️ Epidemics, malnutrition, conflicts, natural disasters, population displacements: ALIMA tackles all dimensions of medical emergencies.
Humanitarian context and challenge
Humanitarian crises: more frequent, more complex
- Health emergencies: rapid spread of epidemics due to mass displacement and collapsed medical infrastructure.
- Armed conflicts: medical facilities are destroyed, staff flee, and civilians are left without care.
- Acute malnutrition: millions of children at risk of death due to lack of adequate care and nutrition.
- Natural disasters: destruction of health facilities, restricted access to care, increased risk of epidemics.
⏳ A rapid response is essential to save lives and limit the impact of humanitarian crises.
ALIMA’s action : emergency medical interventions
💡How does ALIMA respond to emergencies?
ALIMA deploys its multidisciplinary teams from the first days of a crisis to treat the injured, stop the spread of diseases, and strengthen local health systems.
🔹 Epidemic response
🦠 Limiting the spread and treating sick people
- Management of patients with measles, cholera, Ebola, Mpox, Marburg, Lassa fever, malaria.
- Deployment of medical units specialized in the response to viral hemorrhagic fevers.
- Large-scale vaccination campaigns and community outreach efforts.
📌 Example: Since 2014, ALIMA has been responding to Ebola outbreaks across Africa. With innovative treatments and participation in clinical trials, ALIMA, a specialist in viral hemorrhagic fevers, has led key interventions in Guinea, DRC, Uganda, and Equatorial Guinea, using CUBE bio-secure units and training healthcare workers.
🔹Malnutrition: a life-saving emergency for children
🥣 Rapid treatment for severe acute malnutrition
- Distribution of Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF).
- Management of complications in Intensive Therapeutic Nutritional Centers.
- Early detection using the MUAC-Mother approach (mid-upper arm circumference bracelet).
📌 Example: ALIMA has saved thousands of malnourished children across Nigeria and the Sahel.
🔹 Medical care in conflict zones
⚔️ Ensuring access to care despite insecurity
- Treatment of war wounds and trauma.
- Care for affected civilians: pregnant women, children, the elderly.
- Psychosocial support for survivors of violence and displacement.
📌 Example: In the DRC, ALIMA treated the wounded in Goma amid escalation conflict.
🔹Care for displaced populations
🏠 Essential care for families fleeing conflict or disaster
- Emergency medical consultations for refugees and internally displaced persons.
- Access to healthcare for pregnant women and children.
- Vaccination and epidemic prevention in refugee camps.
📌 Example: In Haiti, ALIMA provided life-saving care to thousands of displaced people from Port-au-Prince, despite limited humanitarian and security access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Rapid deployment of specialized teams.
- Collaboration with local authorities to organize care.
- Logistical and medical support to ensure access to healthcare.
- Epidemics (Ebola, cholera, measles, MPOX, Marburg).
- Severe acute malnutrition.
- Armed conflicts and violence.
- Influx of wounded individuals.
- Massive population displacements.
Responses to major crises
- Haiti (2010): Surgery and cholera treatment following the earthquake.
- Mali (2012): Medical and surgical care in response to the conflict.
- Guinea (since 2014): Ongoing fight against Ebola and Covid-19 outbreaks.
- Nigeria (since 2016): Response to nutrition crises and epidemics.
- Democratic Republic of Congo (since 2018): Management of Ebola, Covid-19 and measles outbreaks.
- Burkina Faso (2019): Care for the displaced and mass vaccination campaigns.
Recent interventions (2022-2025)
- 2022
- Ukraine: Support for the Ukrainian healthcare system.
- Uganda: Ebola outbreak.
- Equatorial Guinea: Marburg epidemic.
- 2023
- Nigeria: Diphtheria epidemic.
- 2024
- Haiti: Ongoing intervention.
- Niger: Meningitis epidemic.
- DRC: Mpox epidemic.
- Rwanda: Marburg epidemic.
- Guinea: Diphtheria epidemic.
- 2025
- DRC: Response to an influx of wounded individuals.
On the ground
Related news
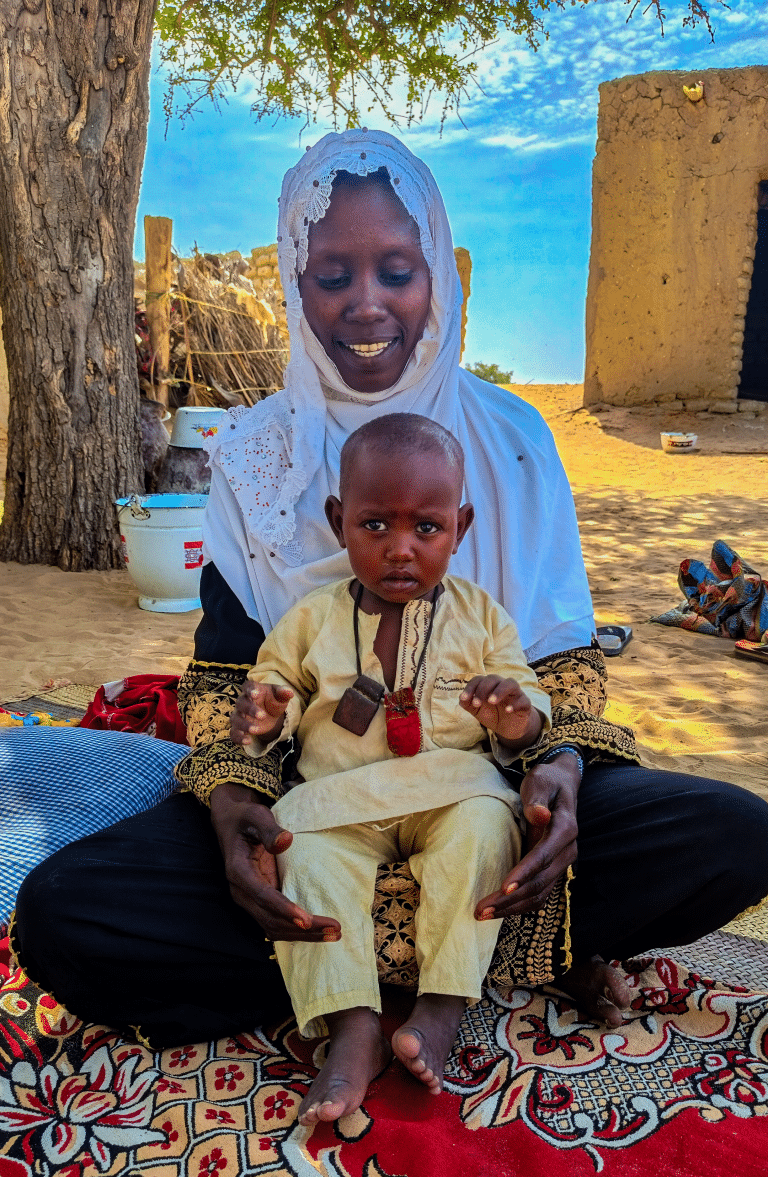
One Sachet, One Chance – Mariam and Hassan’s Journey
In the N’Gouri district, the OptiMAx project combines vaccination with nutritional supplementation to encourage families to return to health centers. Through a mother’s journey, we
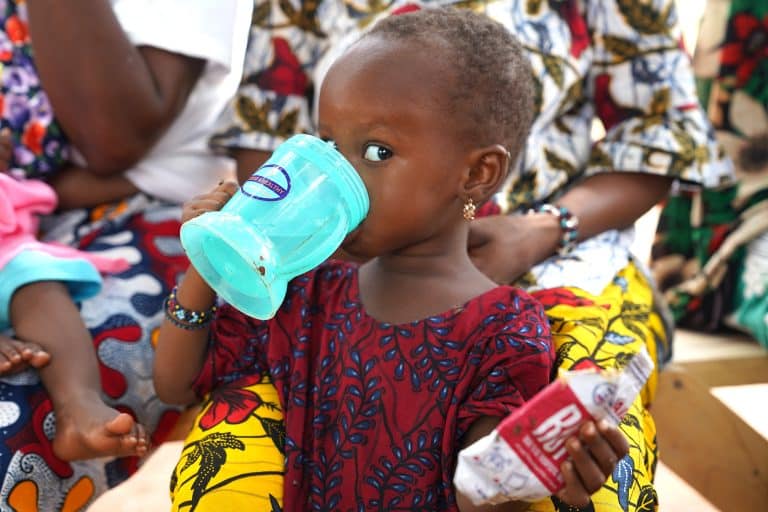

Aminata’s Gaze
Aminata drinks water and clutches a sachet of ready‑to‑use therapeutic food provided through a former USAID-funded program at the mobile nutrition unit run by ALIMA
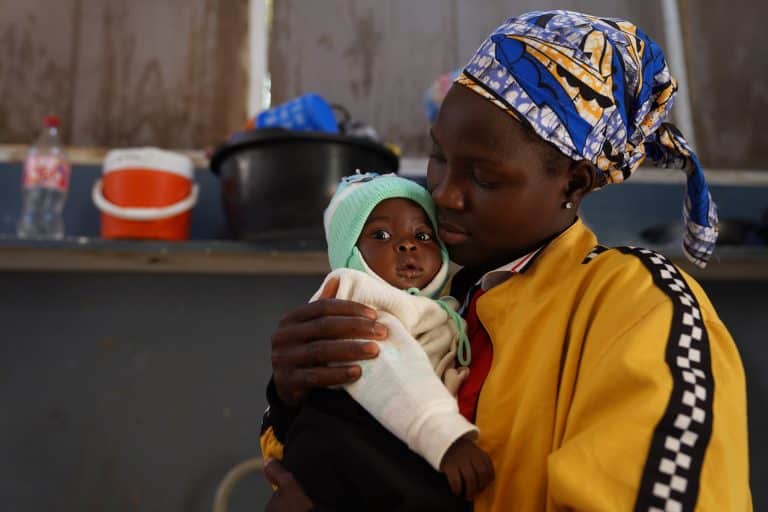

Mokolo: The Day Prisca Started to Get Better
At 20 years old, Adèle Djouanba found far more than medical care for her daughter at the Mokolo Nutrition Center. This young Cameroonian mother shares


