Ebola
Ebola virus disease is a viral but often fatal hemorrhagic fever. Since its discovery in 1976, it has affected several countries in Central, West and East Africa, with major outbreaks, particularly in Guinea between 2013 and 2016.
ALIMA (The Alliance for International Medical Action) plays a key role in the fight against Ebola. In addition to treating patients, the NGO innovates in treatments, prevention, and vaccination to curb the spread of the virus and save lives.
What is Ebola virus disease?
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is an acute viral infection with an average fatality rate of 50% (ranging from 30% to 90% depending on the strain) (WHO). The virus belongs to the filovirus family and is transmitted through direct contact with the body fluids of an infected person or animal.
Origin and transmission of the Ebola virus
Where does the Ebola virus come from?
Named after a river in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where the first outbreaks occurred in 1976, Ebola has since triggered over 20 epidemics across Central and West Africa.
How is Ebola transmitted?
- Animal transmission: fruit bats are suspected of being the natural reservoir of the virus. Contact with infected animals (monkeys, antelopes, porcupines) can lead to human infection.
- Human-to-human transmission: the virus spreads via direct contact with an infected person’s body fluids (blood, sweat, urine, saliva, etc.). It can also be transmitted through unprotected sex or from mother to child through breastfeeding.
- Exposure of healthcare staff: without adequate protection, healthcare workers are particularly at risk.
Essential prevention measures
- Frequent handwashing
- Use of personal protective equipment (masks, gloves)
- Rapid isolation of infected patients
- Community awareness campaigns
- Vaccination
What are the symptoms of the Ebola virus?
Symptoms appear between 2 and 21 days after infection.
Early symptoms:
- High fever (+38°C)
- Extreme fatigue
- Headache and sore throat
Advanced symptoms:
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Rashes
- Internal and external bleeding
Early diagnosis and rapid medical intervention significantly increase the chances of survival.
Take action
Support the fight against Ebola
Your support is crucial to saving lives and preventing future outbreaks.
Ebola treatments and vaccines
Recommended treatments
Since 2022, the WHO recommends two monoclonal antibody treatments proven to be effective against the Zaire strain of Ebola:
When administered early, these treatments increase the chances of recovery.
Vaccines against Ebola Zaire
- rVSV-ZEBOV: demonstrated 100% efficacy in a 2015 trial in Guinea.
- Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo (Janssen): WHO-validated to strengthen protection.
Ongoing studies, such as PREVAC, led by ALIMA and its partners, continue to optimize vaccine strategies.
ALIMA's commitment in the fight against Ebola
Actions on the ground
Since 2014, ALIMA has been actively involved in the outbreaks in the DRC and Guinea:
- Establishment of Ebola Treatment Centers (ETCs)
- Diagnosis and patient care
- Community awareness campaigns
- Training of health workers
A major innovation: the CUBE
ALIMA has developed the Biosecure Emergency Room for Epidemics (CUBE), a care unit to isolate and treat patients while limiting risks for caregivers.
In 2019, Bill Gates awarded ALIMA the “Game-Changing Innovator” prize at the Reaching the Last Mile Forum in Abu Dhabi.
ALIMA, a key player in Ebola research
In collaboration with INSERM, the WHO, and other partners, ALIMA participates in several research programs aimed at:
- Improving treatments
- Optimizing vaccination strategies
- Reduce mortality rates
The PALM study, to which ALIMA contributed in the DRC, demonstrated that early treatment can lower mortality rates to below 10%.
Our reports and publications on Ebola
ALIMA conducts committed scientific research, grounded in the realities of the field.
| Publication Title | Link | Authors | Journal | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo-Controlled Trial of Tecovirimat for Endemic Mpox | Read the publication | The PALM007 Writing Group | The New England Journal of Medicine | 2025 |
| Safety and immunogenicity of the two-dose heterologous Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo Ebola vaccine regimen in infants | Read the publication | Choi E.M., Lacarra B., Afolabi M.O., et al. | The Lancet Global Health | 2023 |
| Randomized Trial of Vaccines for Zaire Ebola Virus Disease | Read the publication | PREVAC Study Team, Kieh M., Richert L., et al. | The New England Journal of Medicine | 2022 |
| Development of the PREDS score to predict in-hospital mortality of patients with Ebola virus disease | Read the publication | Jaspard M., Mulangu S., Juchet S., et al. | eClinicalMedicine | 2022 |
| Post-exposure prophylaxis following high-risk contact with Ebola virus, using immunotherapies with monoclonal antibodies | Read the publication | Jaspard M., Juchet S., Serra B., et al. | International Journal of Infectious Diseases | 2021 |
| Optimisation du standard de soins pour les patients atteints de maladie à virus Ebola en République Démocratique du Congo en 2019 | Read the publication | Jaspard M., Juchet S., Serra B., et al. | Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses | 2020 |
| The evolution of supportive care for Ebola virus disease | Read the publication | Lamontagne F., Clément C., Kojan R., et al. | The Lancet | 2019 |
| Shifting the Paradigm — Applying Universal Standards of Care to Ebola Virus Disease | Fischer W.A., Crozier I., Bausch D.G., et al. | New England Journal of Medicine | 2019 | |
| A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Ebola Virus Disease Therapeutics | Read the publication | Mulangu S., Dodd L.E., Davey R.T. Jr., et al. | New England Journal of Medicine | 2019 |
| COMMENT: The evolution of supportive care for Ebola virus disease | Read the publication | Lamontagne F., Clément C., Kojan R., et al. | The Lancet | 2019 |
| Prevention of Ebola virus disease through vaccination: where we are in 2018 | Read the publication | Lévy Y., Lane C., Piot P., Beavogui A.H., et al. | The Lancet | 2018 |
| FRONTLINE: a new treatment facility for Ebola virus disease | Sharmila Devi | The Lancet | 2018 | |
| FRONTLINE: a new treatment facility for Ebola virus disease | Sharmila Devi | The Lancet | 2018 | |
| Persistence du virus Ebola dans l’environnement d’un centre de traitement en Guinée forestière | Read the publication | Palich R., Irenge L., Barte de Sainte Fare E., et al. | Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses | 2016 |
| Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for Ebola Virus Disease (the JIKI Trial) | Read the publication | Sissoko D., Laouenan C., Folkesson E., et al. | PLoS Medicine | 2016 |
| A 6-Year-Old Child with Severe Ebola Virus Disease: Laboratory-Guided Clinical Care in an Ebola Treatment Center in Guinea | Read the publication | Palich R., Gala J.-L., Petitjean F., et al. | PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases | 2016 |
| Clinical, Virological and Biological Parameters Associated with Different Outcomes of Ebola Virus Infection in Macenta, Guinea | Vernet M.A., Reynard S., Fizel A., et al. | The Lancet Infectious Disease (in submission) |
On the ground
Related news
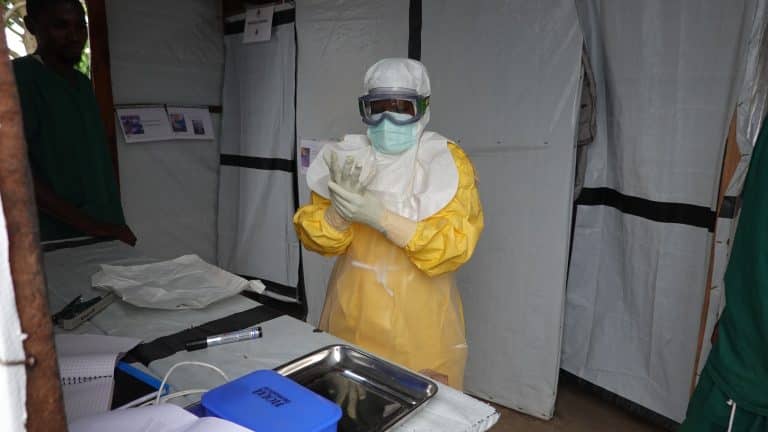
Three Months to Eradicate Ebola: The Power of Collective Action in Kasai
After three months of collective mobilization, the 16th Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was declared over on November 30, 2025.
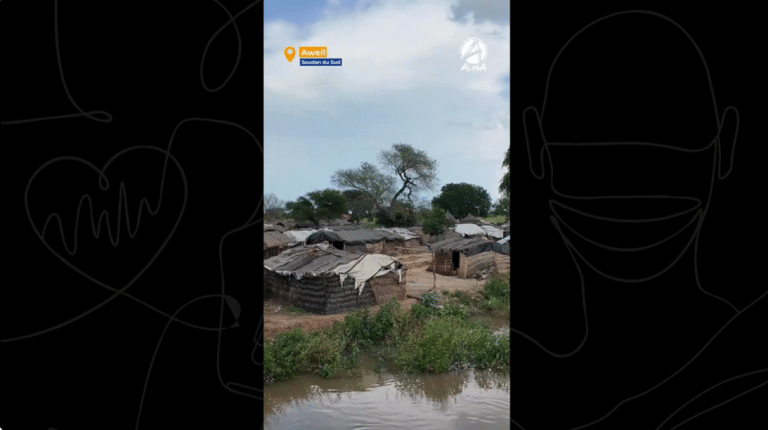

South Sudan: when the climate crisis becomes a health crisis
In Aweil, recurring floods cut off entire villages. Malaria, diarrhea, pneumonia: children are on the front lines. Since 2025, ALIMA has been deploying an emergency
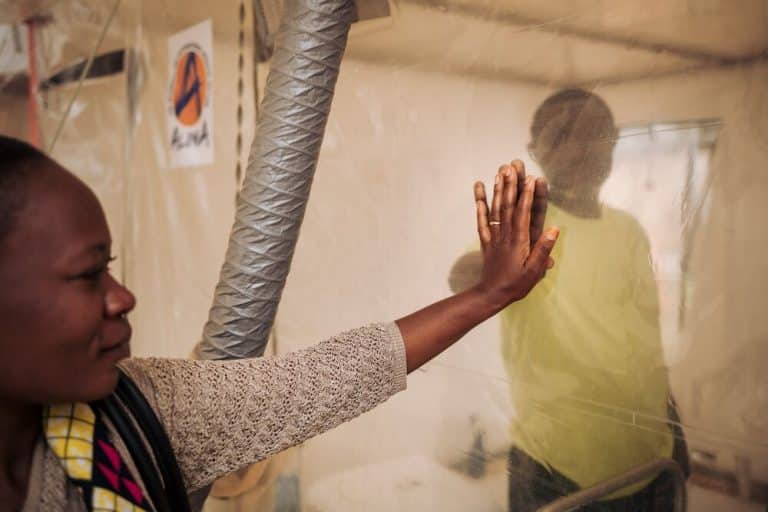

Ebola in Kasai: A Race Against Time!
Since late August, a new Ebola outbreak has struck Kasai in the Democratic Republic of Congo. With 40 deaths already and more than 1,400 contacts


